Land Operations – ISR Missions – Reconnaissance
ISR synchronizes and integrates the planning and operation of sensors, assets, and processing, exploitation, dissemination systems in direct support of current and future operations. UAS ISR missions are broadly considered tactical air reconnaissance or surveillance.
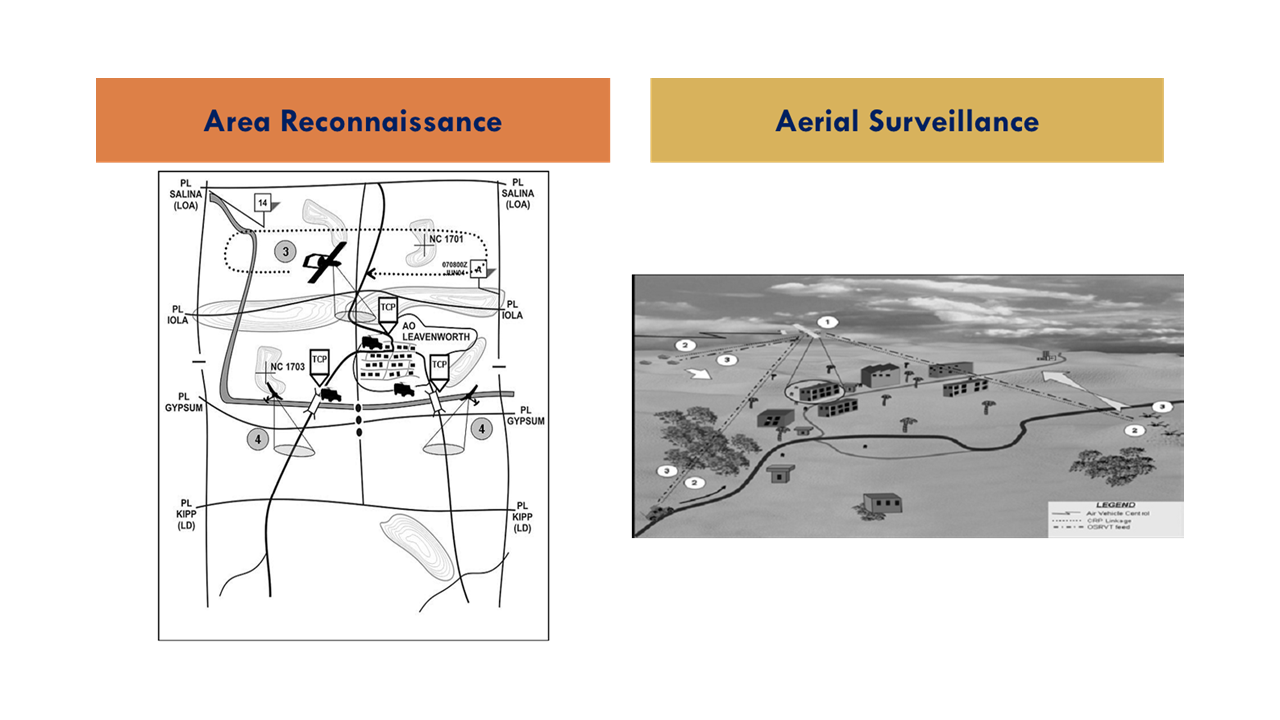
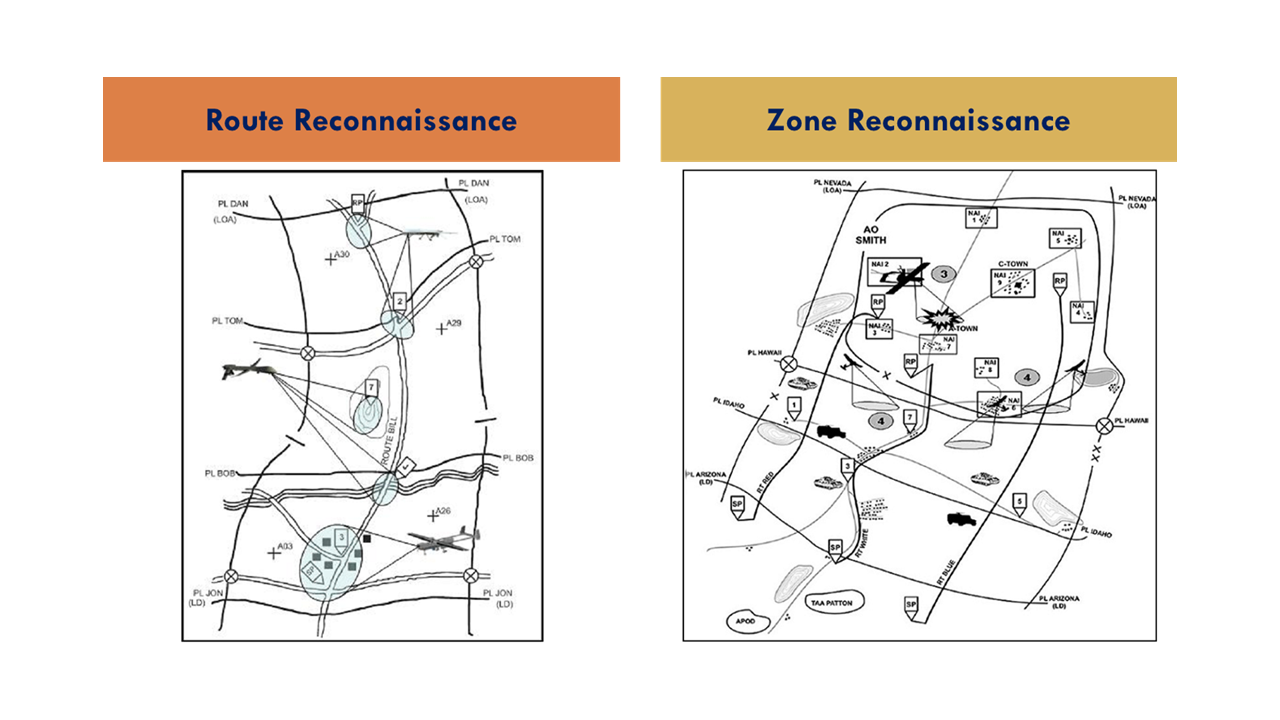
Route Reconnaissance – Is the directed effort to obtain detailed information of a specified route and all terrain from which the enemy could influence movement along that route. UAS, with multi-sensor capabilities, are well suited to reconnoiter the front, flanks, and rear providing early warning, ambush detection, and over watch. Additional UAS support roles are ground element over watch, traffic ability assessment, and landing site and hazard location, threat, and suspicious item identification. The best results occur when synchronized and commanded by ground elements.
Zone Reconnaissance – Is the directed effort to obtain information concerning all routes, obstacles, terrain, enemy forces within a zone defined by boundaries. Used when existing knowledge of terrain is limited, combat operations have altered the terrain, boundaries are restricted or when the enemy situation is vague. Often time consuming, and covering extensive distances ahead of ground forces in well-coordinated zones which dictates special considerations for air assets. Planning considerations are similar to route reconnaissance though multiple teams (manned and unmanned) operate abreast.