In radiolocation, the system is used to determine the position of targets in space
spherical or cylindrical coordinates. The most widely used is the spherical coordinate system. In this
system the position of the target is determined by the following three coordinates: inclined distance D,
azimuth β and elevation angle ε. The origin of the spherical coordinate system is represented by the place of
arrangement of the radar O. The figure shows the coordinates of a target located at point T.
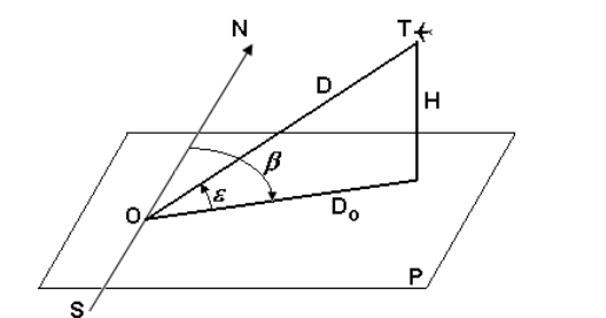
- Target coordinates
The inclined distance is the distance in a straight line between the radar and the target.
Azimuth is the angle measured at the location of the radar between the north direction
geography and the projection of the inclined distance in the horizontal plane P. The value of the azimuth is calculated
clockwise, from 0 ° to 360 °, originating, as I said before, the direction
geographical north.
The elevation angle, sometimes called the elevation angle, is the angle between the direction
the distance inclined to the target and its projection on the horizontal plane P. In the case of radars based on
ground this plane P is tangent to the surface of the earth at the location of the radar.
The three coordinates of the spherical system can be determined directly. The inclined distance is
calculates by measuring the delay time of the survey signal, ie the time required
the signal to move from the radar to the target and back, according to the formula
To determine the angular coordinates (azimuth and elevation angle), antenna
The radar must be directive, ie have a very narrow directivity feature
the plane corresponding to the coordinate being measured (horizontal for ß, vertical for ε). This one
Narrow directivity feature is shifted in that plane, and when
the antenna is in the direction of the target, the signal reflected from it is maximum. At this point
measures the respective coordinate by means of a device mechanically coupled to the antenna axis. This
The type of method for determining angular coordinates is called the amplitude method and
it is of several kinds: the method of maximum, minimum and equal signal area.
Knowing the three spherical coordinates can determine other coordinates, such as
horizontal distance Do and target height H:
Do = D X COS ε
H = D X sin ε
Horizontal distance is the projection of the inclined distance in the horizontal plane P. Azimuth,
the height and the horizontal distance form the cylindrical coordinate system, which is used
sometimes instead of spherical.
In the above formula the height was calculated from the horizontal plane P. Taking in
Considering the curvature of the Earth, the calculation of the height relative to the ground surface is done with the help
expression:
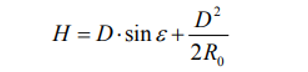
where Ro is the equivalent radius of the Earth.