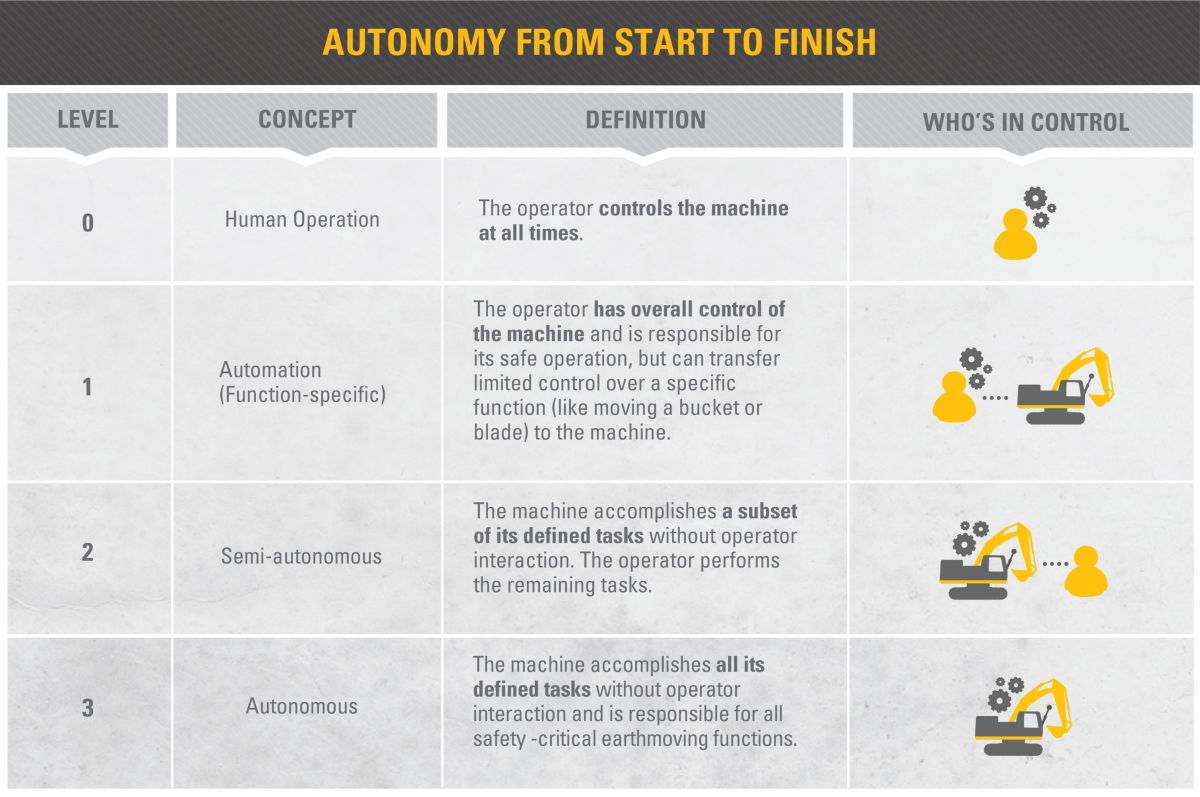
In the case of defining autonomous systems, the most common approach includes the criterion of the degree of human control over a machine (human-machine relation). This categorization distinguishes semiautomatic systems (“human in the loop”), in which the automatic operation is possible until certain moment and then the human intervention is necessary. For example, weapon systems may independently affect the targets that have been previously selected and approved for combat by a human (operator). This type of armament includes various types of guided ammunition, also the “fire-and-forget” type .
The second group covers supervised systems (“human on the loop”), in which there is a possibility of uninterrupted autonomous operation, but with the possibility of human intervention at any given moment. Weapon systems from this group are able to select and combat targets on their own, from the moment they were activated. However, the operator of such weapon system has the knowledge about what kind of objects can be targeted and the operator may intervene at any time by interrupting the process. In practice, these types of weapon systems (supervised) are used in defensive operations and in undemanding operational environment. They react directly to the defined threats, where the reaction of a human (operator) could be too slow, and in the case of doubtful situations the operator may react at any time.
The third group consists of fully autonomous systems (“human out of the loop”), without the possibility of human intervention. They refer to weapon systems that independently, without human participation, are able to select and combat targets in a previously defined geographical region, time interval and according to the adopted rules. The operator does not know what targets will be selected for combating, but it should be remembered that the types of combated objects have been previously defined by a human according to the specific criteria. In other words, a man decides earlier in what manner the autonomous combat system will carry out its tasks.