Comparative analysis
|
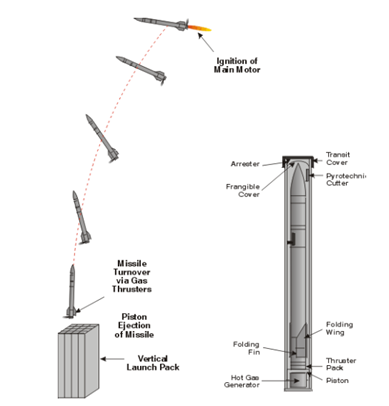
Soft Vertical Launch Soft vertical launch (SVL), in contrast to more conventional VL systems, ignites the rocket motor after the missile has been launched and directed towards the target. The GBAD concept is illustrated in Figure 1. The missile is ejected from the launch tube by a piston driven by means of hot or cold gas, similar to an ejection seat. MBD are developing a powered piston approach that allows the missile ejection to be more precisely controlled such that the missile is subjected to much lower launch loads and requires less energy to complete the launch event. The piston is caught and retarded before it leaves the canister. The ejection system imparts the missile with an exit velocity allowing it to achieve the optimum turnover altitude within the required time. All ejection effects are contained in the canister. All ejection loads are transferred through the canister down to the surface. For GBAD, the missile is turned over towards the target predicted intercept point by means of a solid propellant, rocket powered, thruster providing lateral control in pitch, yaw and roll. Once turned over, the missile boost motor is then ignited. A smoother and more direct missile turnover is possible enabling rapid target acquisition, by the seeker, for minimum range engagements. |
 |
|
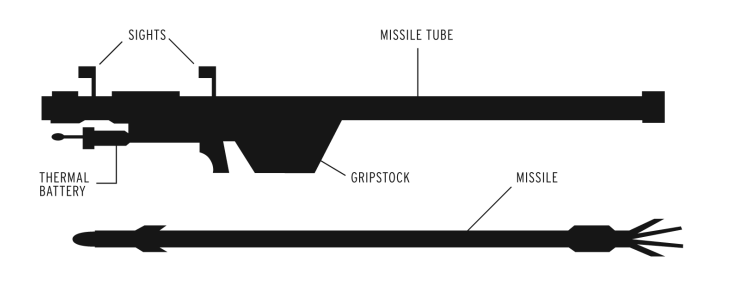
MANPADS launcher In basic terms, the typical MANPADS system consists of: a missile packaged in a tube which includes a seeker head, a launching mechanism commonly called a “gripstock,” and a battery. Under optimum conditions, an expert operator can assemble, shoulder, and launch a missile in 30 seconds. Most versions are effective against fast-moving targets up to 15,000 +/- feet in altitude and three-to-five miles in range. Once launched, a MANPADS tracks and impacts its target in approximately five seconds. Most accelerate to velocities approximately twice the speed of sound, Mach 2, in less than two seconds and maneuver at G-loadings far greater than any transport category aircraft is capable of attempting. While they vary tremendously in terms of capability, most use an infrared (IR) seeker to detect an aircraft’s IR signature against the cold sky and home into the heat emitted from hot metal sections of the aircraft engines and exhaust. The seeker head of a MANPADS serves as its brains and defines the overall system in terms of guidance. Three main types of seekers exist including IR, command line-of-sight (CLOS) - meaning radio controlled, and laser beam riders. |
 |