Comparative analysis
|
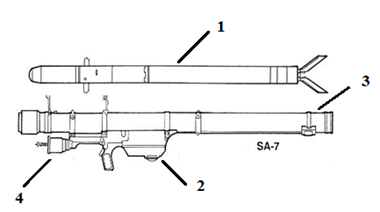
CA-94 SA-7 'Grail' is used for destruction of the enemy's means of air attack at low altitude and in conditions of direct visibility. In basic terms, MANPADS system consists of: (1) a missile packaged in a tube which includes a seeker head, (2) a launching mechanism commonly called a “gripstock,” and (3) a battery (Figure 1). Under optimum conditions, an expert operator can assemble, shoulder, and launch a missile in 30 seconds. Most versions are effective against fast-moving targets up to 15,000 +/- feet in altitude and three-to-five miles in range. The main component parts are (Figure 2): - self-guided missile (1); - launch mechanism IL-01 (2); - launch tube IL-02 (3); - ground power supply BT-A-94 (4). |
 |
|
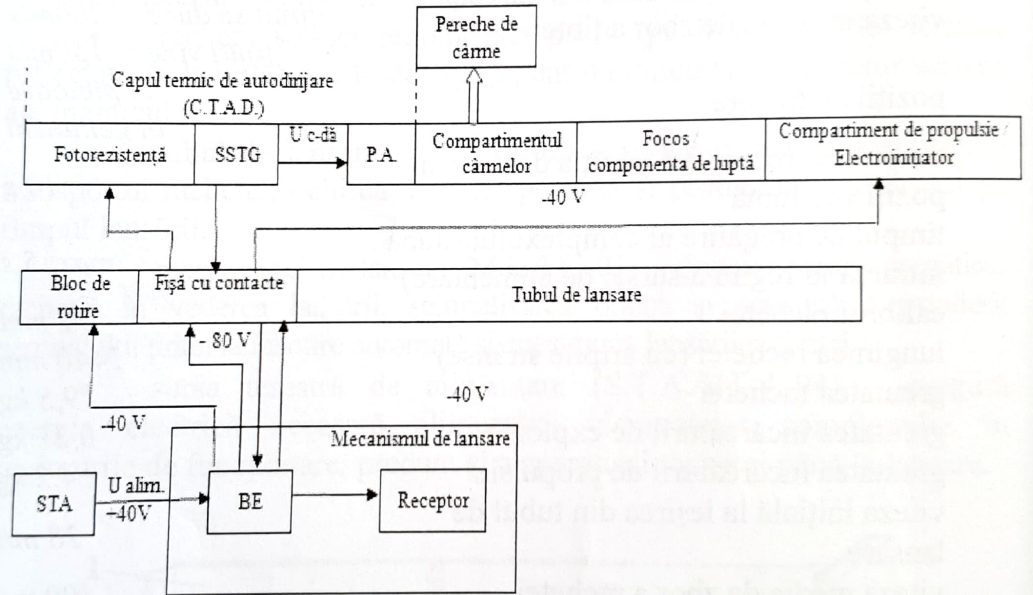
Combat use: Seeker, passive, thermal, tracking, and narrow-field, automatically accompanies the target and forms the control signal proportional to the angular velocity of the line of sight. It is a gyroscopic tracking system that keeps the coordinator's optical axis in the direction of the target uninterrupted. The autopilot converts the control signals from the electronic block output to the control signals for the rudder rudders. The rudder compartment is the element that houses the missile flight control equipment and the power supply board. The rudder machine is a gas amplifier of the electrical control signals from seeker, and executes the change of the position of the aerodynamic rudders in the process of missile flight. The GPS supplies the missile's on-board equipment with in-flight power. The shrapnel, fugitive and cumulative action-packed cargo that destroys aerial targets through shrapnel and shock waves, is initiated by the warhead when the missile meets the target or self-destructs. The warhead is of the electromagnetic type, with a target impact sensor, remote arming and a self-destruct mechanism. The solid fuel propulsion system launches the missile from the launch tube, imparts a rotational motion to it, accelerates it to an average speed of 500 m/s and keeps it in flight. The starting engine throws the missile from the tube at a speed of 28 m/s and prints a speed around its axis of 20 rpm. After 0.3 sec. In flight, the radiation initiator ensures that the marching engine starts and imparts a speed of 500 m/s to the missile, maintaining it during the flight. If the missile does not reach the target, after 14-17 s from the launch, the delay ring burns and the electric detonator starts operating, which causes the destruction of the missile. |
 |
|
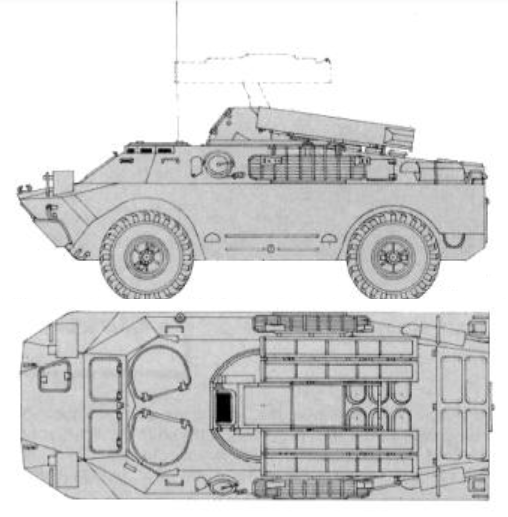
The SA-9 Gaskin (Russian name 9K31 Strela-1) is a highly mobile, short-range, low altitude infra-red guided surface-to-air missile system mounted on the wheeled armoured vehicle BRDM-2. The first Strela-1 (SA-9/`Gaskin') launchers were produced in 1966 with the system attaining operational status in 1968. The CA-95 is intended for the destruction of aircraft, projectiles, light bombs and other low-flying aerial targets. It is used as a means of anti-aircraft defense of land units and subunits and for the direct defense of certain objectives. The system is based on the BRDM-2 4x4 chassis (Figure 3). The driver and commander are seated in the front and the gunner in the turret. Up to four launch container can be attached to the turret. During travel the missiles are lowered. The system is a stand-alone system, but usually it operates in pairs or groups of four. Target information is relayed by radio by other air defense systems. The turret is fitted with four surface to air missiles with infrared guidance. The maximum effective range is 4.2 km and maximum altitude is 3 km. Due to the limitations of the seeker the maximum range can only be achieved under favorable circumstances. Effectiveness during head-on engagements and at night is much reduced. The steel armor protects from small arms fire and shell splinters. The system is operated under full armor protection, except for reloading the missiles. An NBC system is fitted while smoke grenade dischargers are not. |
 |
|
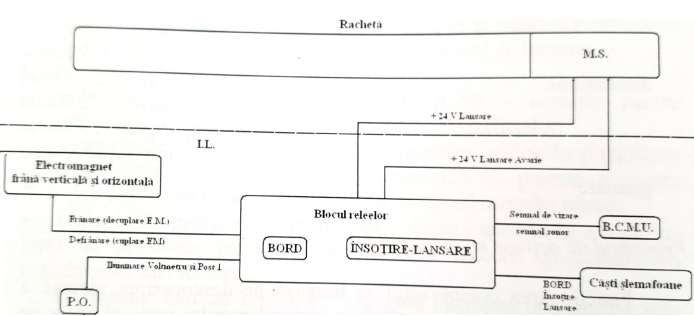
Combat use: The principle of operation of the CA-95 complex is based on the visual detection of aerial targets and the self-guided missile to the target using the self-steering head. Upon receipt of the combat command, the operator switches the launcher to the combat position, attempting to visually detect the target. Aiming is done first approximately with the mechanical sight, and then the exact sighting is performed with the sighting device. After superimposing the reticle of the sighting device with the aerial target, the operator presses the “ACCOMPANY - LAUNCH” button until stage I, operation by which the container box is opened and the aerial target is caught by seeker. By pressing the “ACCOMPANY - LAUNCH” button until the second stage, the missile launch takes place, after which the operator releases the button and executes a new catch of the air target. In flight, the missile is powered by the on-board power supply. The target is destroyed by the missile's payload when it hits the air target directly or passes less than 5 m from the target |
 |