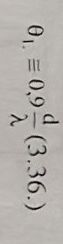Angular coordinates in radiolocation
Methods for determining angular coordinates in radiolocation.
Radio stations, in order to determine the position of the targets in space, must determine not only the distance but also the direction in which the target is located. This is usually done by determining two angular coordinates:
- azimuth: The absolute (real) azimuth of a radar target is the angle between the North direction and the target direction. This angle is measured horizontally and clockwise, starting as a reference from the North direction (azimuth 0). (In the case of radars placed on ships or aircraft, the azimuth of a target can be measured by reference to the direction of travel of the ship or aircraft; in this case it is called the relative azimuth.) For accurate azimuth determination, accurate of the North direction. In the case of older radars, this requires additional operations, requiring the use of a compass or certain trigonometric calculations. Modern radar systems automatically determine this direction, using the GPS system. It is denoted by "B".
- elevation angle: The angle between the direction of the target and the horizontal plane passing through the position of the radio station and denoted by "E"
Directional antennas are used to determine the angular coordinates, whose directivity characteristics are expressed by the ratio between the radiated power in a certain direction and the maximum power.
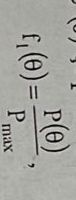
The width of the directivity characteristic is the angle limited by the lines passing through the points where the power decreases to half of the maximum value. Radio stations use different types of antennas: with parabolic reflector, wave channel, chimney.
The directivity characteristic for antenna dimensions of (4-5) λ, if a uniform radiation is considered, is given by the relation:
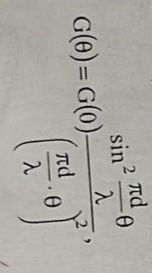
d-the diameter of the antenna in the plane in which the characteristic rises
Θ-the measured angle with respect to the maximum radiation direction
The width of the directive feature is: