Parameters of radar systems
The parameters of radar systems are divided into two categories: tactical and technical parameters.
Tactical characteristics are those parameters that assess the possibility of radar to
fulfill the mission. Technical parameters characterize the technical state of the radar system, they can
be measured directly by means of measuring instruments. Next we will present the main ones
parameters of radar systems, customized for circular and emission observation radars in
pulses.
Tactical parameters
The main category of tactical parameters is the radar action area, or
the area of observation. This is the space within which the radar performs its role,
that is, it discovers targets with the imposed values of false discovery and alarm probabilities.
The characteristics of the observation area are determined by the destination of the radar. What parameters
characterize the area of action are:
-the maximum distance of discovery Dmax, respectively the minimum distance of discovery Dmin;
-the minimum εmin angle and the maximum εmax elevation angle;
-maximum height of discovery Hmax and minimum height of discovery Hmin;
-the radius of the dead cone Rcm.
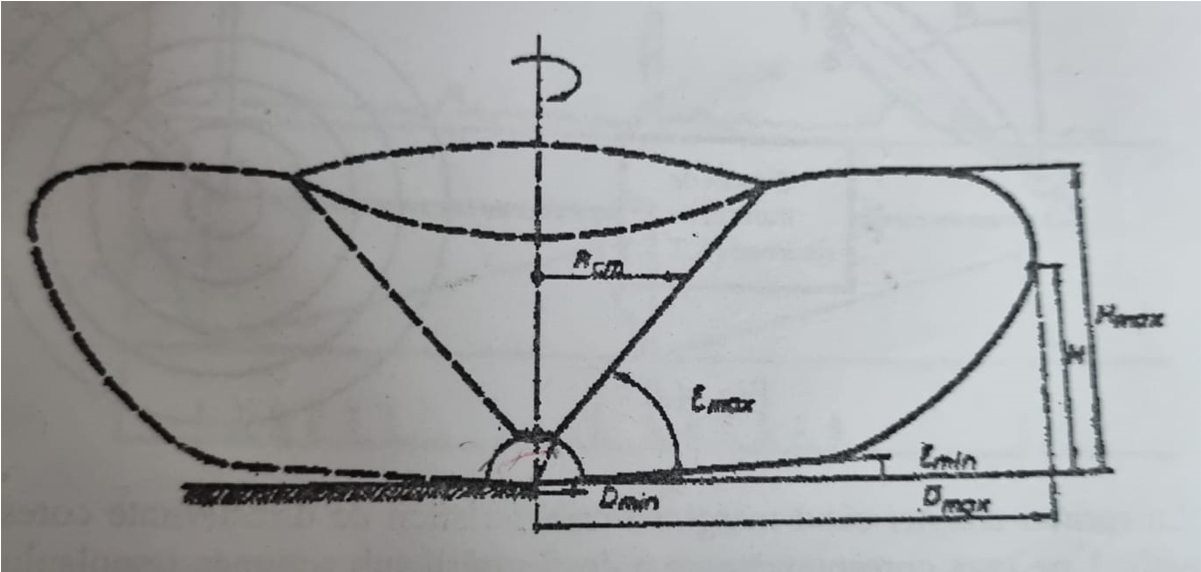
The maximum distance is given by the radiolocation equation, but it is conditioned by the period of
repetition of impulses, as we will see later. Because of the shape of the area discovery is given by the form of the characteristic of directivity, the value of the maximum distance depends and the flight height of the target.
Since during the emission of the survey pulses the reception is blocked, the minimum distance is determined primarily by the duration of the survey pulses:
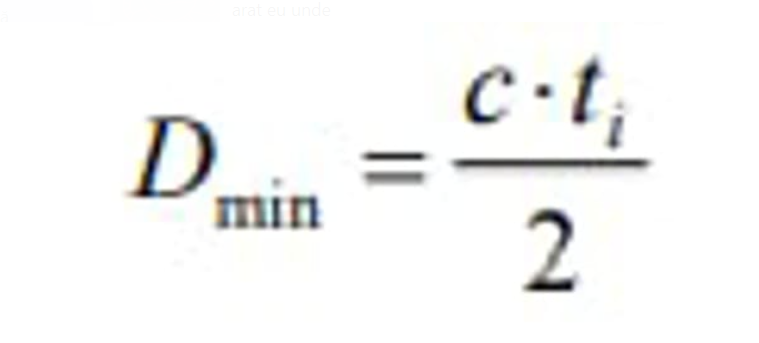
The value of the minimum distance from discovery also depends on other factors, such as time restoring the antenna switch. If different antennas are used for broadcasting, and Reception, the minimum distance is practically negligible. The radius of the dead cone is a function of the maximum angle of elevation and the height of the target, it can be determined by means of the formula:
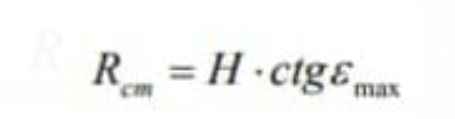
Another parameter that characterizes the radar's area of action is the possibilities inclination of the directivity characteristic, influencing the values of the minimum and maximum angle of ascension and of the maximum and minimum height of discovery.
The minimum height of discovery is dependent on the minimum angle of the directivity. Its value can be optimized by arranging the radar antenna at a height higher and downward inclination of the feature of directivity. The period of observation of space represents the time of the necejump for the diagram of directivity to explore the entire area of discovery. On circular observation radars, this parameter is given by the rotational speed of the antenna Ω. A high rotation speed of the antenna ensures a faster refresh of target information. Another tactical feature is the separation capability or resolution. It represents the radar's ability to ensure separate detection and display of two very close targets one by the other. The resolution shall be defined for each type of coordinate. The distance separation capability is the minimum distance between two targets on the same steering from the radar at which the targets are still detected and displayed separately. Its value depends on the duration of the survey momentum.
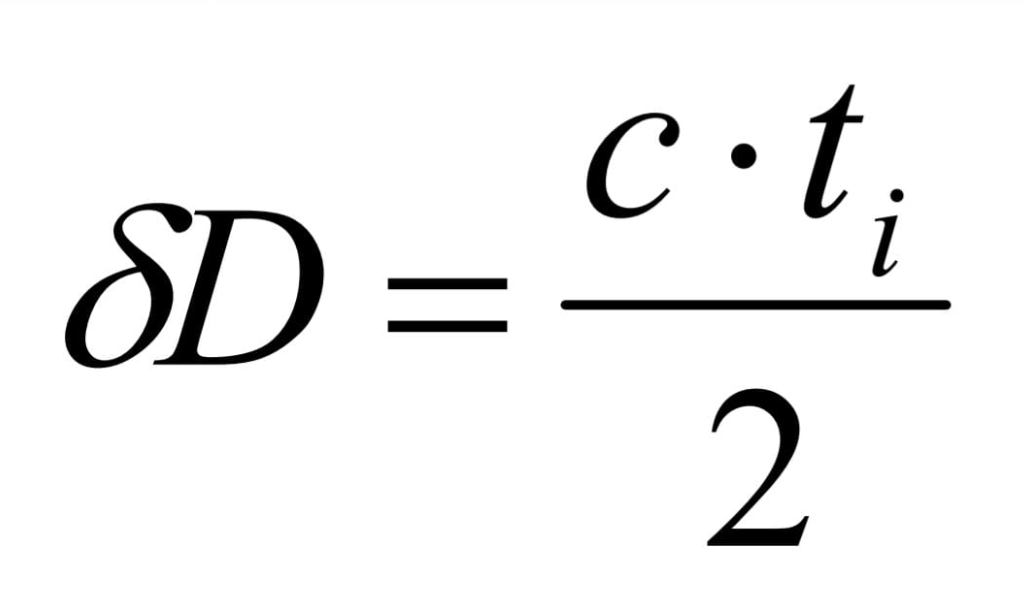
If two targets are in relation to each other at a distance less than the capacity of separation in distance then the impulses reflected by each target overlap and so the targets do not they can also be seen separately.
The separation capability in angular coordinates represents the minimum angle between directions to two targets at the same distance from radar where targets are still observed separately. It is expressed for each angular coordinate, azimuth and ascension angle: δβ and δε . The value of the angular separation capability depends mainly on the width of the
directivity in that plan.
Other tactical paramenters are:
- accuracy of the determination of coordinates,
-jamming stability is a very important parameter of radars with military destination, representing the radar's ability to carry out its mission under the conditions of an environment electromagnetic hostile; it is given by the possibilities of attenuation and elimination of different signals
Disruptive
- the reliability or safety in operation is mainly characterised by the following parameters:
•mean time between failures (MTBF) average operating time, the duration of operation without malfunctions;
•mean time to repair (MEAN TIME TO REPAIR) (MTTR );
• availability
Mobility and transportability of radar, which include the weight of the system, the dimensions, the number of transport units, the routes by which it can be transported, etc.;
• The time of tightening and unfolding, i.e. the time required to switch from the configuration
transport to the operational one and vice versa;
• Coupling time;
•Power supply possibilities: supply voltage parameters,
the power consumed, the consumption of the generating set, etc.;
• Weather conditions in which it can operate: temperature, wind speed,
Humidity, altitude;
• Processing capacity, i.e. the number of targets discovered and processed simultaneously,
During each period of observation;
• The possibilities of integration in command and control systems, the most important being
the type of communication links used and the format of the data transmitted.